This website provides guidance to Grade 6 students undertaking Digital Technology. By presenting support in the digital technology context of Materials and technologies specialisations through an assignment intended to encourage “ethical and sustainable decisions about designed solutions and processes by learning about and working with materials and production processes” (Australian Curriculum, Assessment and Reporting Authority, 2019). This will be achieved through their assignment presenting the task of creating and designing a recycled and repurposed fashion design for their own class fashion show.
This page provides my initial draft outline of design brief, the Queensland Curriculum, and references used.
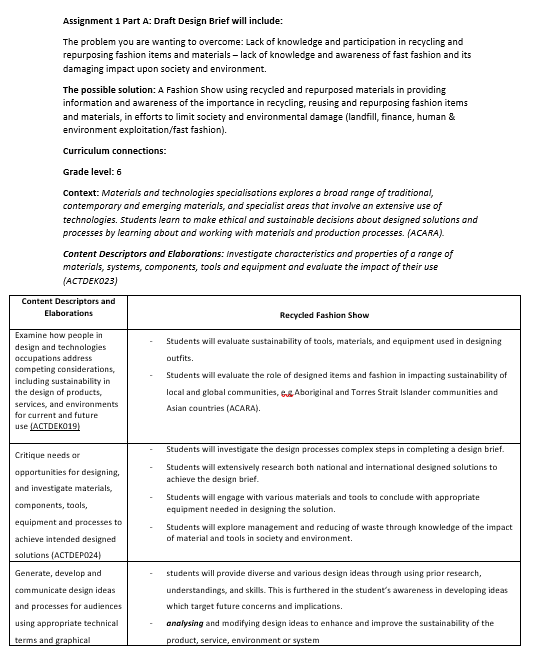
Initial Design Brief Draft:
Australian Curriculum Context:
Materials and technologies specialisations:
“Materials and technologies specialisations explores a broad range of traditional, contemporary and emerging materials, and specialist areas that involve an extensive use of technologies. Students learn to make ethical and sustainable decisions about designed solutions and processes by learning about and working with materials and production processes” (Australian Curriculum, Assessment and Reporting Authority, 2019).
Technologies context – Australian Curriculum:
Content Descriptors:
Investigate characteristics and properties of a range of materials, systems, components, tools and equipment and evaluate the impact of their use (ACTDEK023)
Elaborations:
- identifying the properties of materials for the design and construction of a sustainable household item, for example a product for storing harvested water
- evaluating the functional properties of a specific-purpose household system, for example a security system
- examining the materials and systems used in a public use system that affect the way people live, for example a community exercise environment or arts facility, water treatment, garbage collection
- comparing tools, equipment and techniques to select those most appropriate for a given purpose
- evaluating the use of computer-aided manufacturing in terms of cost and impacts on local and regional designers, producers and enterprises
- comparing the design and production of products, services and environments in Australia and a country in the Asia region
Creating Designed Solutions – Australian Curriculum:
Investigating:
Examine how people in design and technologies occupations address competing considerations, including sustainability in the design of products, services, and environments for current and future use (ACTDEK019)
Elaborations
- reflecting on the features of designed solutions that ensure safety and wellbeing of users, for example smoke alarms
- evaluating the sustainability implications of materials, systems, components, tools and equipment, for example materials can be recycled or re-used to reduce waste; systems may benefit some, but disadvantage others
- considering the impact designed products, services or environments have in relation to sustainability and also on local, regional and global communities, including Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities and countries in the Asia region
- reflecting on the importance of aesthetics, function and sustainability in product design, for example a textile product that gives protection and is appealing; a motor that moves a vehicle and uses a sustainable power source
- identifying the components of a service or system that contribute to its success and assessing potential risk or failure, for example, communication in the school or communication of a message to a wide audience; a system that manages an aspect of the environment; a campaign such as Clean Up Australia Day in different communities
- identifying the impact of the designed features of an environment, for example a modification to a home to reduce environmental impact; restoring a natural environment and retaining access for the public
Critique needs or opportunities for designing, and investigate materials, components, tools, equipment and processes to achieve intended designed solutions (ACTDEP024)
Elaborations:
- exploring the steps involved in the process to satisfy a design brief, need or opportunity
- investigating designed solutions from around the world to make suitable, quality decisions that meet the design brief, challenge or scenario
- identifying the importance of complementary parts of working, everyday systems by deconstructing the components, structure and purpose of products, services or environments
- testing a range of materials, components, tools and equipment to determine the appropriate technologies needed to make products, services or environments, for example a moving vehicle
- investigating how to minimise material use and manage waste by critiquing the environmental and social impacts of materials, components, tools and equipment
Generating/ Producing:
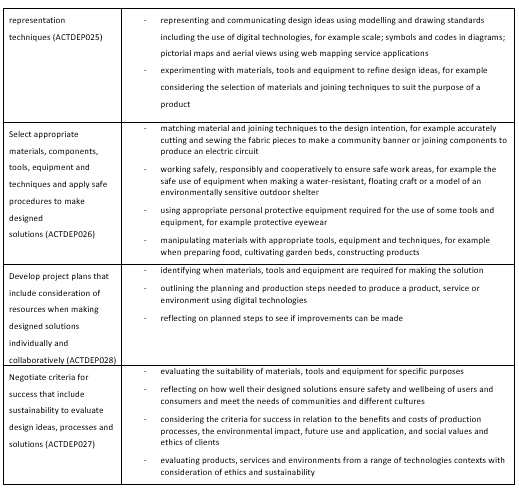
Generate, develop and communicate design ideas and processes for audiences using appropriate technical terms and graphical representation techniques (ACTDEP025)
Elaborations
- generating a range of design ideas for products, services or environments using prior knowledge, skills and research
- developing alternative design ideas and considering implications for the future to broaden the appeal and acceptance of design ideas
- analysing and modifying design ideas to enhance and improve the sustainability of the product, service, environment or system
- representing and communicating design ideas using modelling and drawing standards including the use of digital technologies, for example scale; symbols and codes in diagrams; pictorial maps and aerial views using web mapping service applications
- experimenting with materials, tools and equipment to refine design ideas, for example considering the selection of materials and joining techniques to suit the purpose of a product
Select appropriate materials, components, tools, equipment and techniques and apply safe procedures to make designed solutions (ACTDEP026)
Elaborations:
- matching material and joining techniques to the design intention, for example accurately cutting and sewing the fabric pieces to make a community banner or joining components to produce an electric circuit
- working safely, responsibly and cooperatively to ensure safe work areas, for example the safe use of equipment when making a water-resistant, floating craft or a model of an environmentally sensitive outdoor shelter
- using appropriate personal protective equipment required for the use of some tools and equipment, for example protective eyewear
- manipulating materials with appropriate tools, equipment and techniques, for example when preparing food, cultivating garden beds, constructing products
Planning and Managing:
Develop project plans that include consideration of resources when making designed solutions individually and collaboratively (ACTDEP028)
Elaborations
- matching material and joining techniques to the design intention, for example accurately cutting and sewing the fabric pieces to make a community banner or joining components to produce an electric circuit
- working safely, responsibly and cooperatively to ensure safe work areas, for example the safe use of equipment when making a water-resistant, floating craft or a model of an environmentally sensitive outdoor shelter
- using appropriate personal protective equipment required for the use of some tools and equipment, for example protective eyewear
- manipulating materials with appropriate tools, equipment and techniques, for example when preparing food, cultivating garden beds, constructing products
Evaluation:
Negotiate criteria for success that include sustainability to evaluate design ideas, processes and solutions (ACTDEP027)
Elaborations
- independently and collaboratively identifying criteria for success, processes and planning, for example using visual representations such as a flowchart
- evaluating the suitability of materials, tools and equipment for specific purposes
- reflecting on how well their designed solutions ensure safety and wellbeing of users and consumers and meet the needs of communities and different cultures
- considering the criteria for success in relation to the benefits and costs of production processes, the environmental impact, future use and application, and social values and ethics of clients
- evaluating products, services and environments from a range of technologies contexts with consideration of ethics and sustainability
References & Resources
Australian Curriculum, Assessment and Reporting Authority (2019). Structure. [online] Australiancurriculum.edu.au. Available at: https://www.australiancurriculum.edu.au/f-10-curriculum/technologies/design-and-technologies/structure/ [Accessed 29 Mar. 2019].
i-D (2019). A Beginner’s Guide To Sustainable Fashion. [online] YouTube. Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YqOKsiTc9fs [Accessed 29 Mar. 2019].
Kids Academy Company. (2019). Recycling for Kids | Recycling Plastic, Glass and Paper | Recycle Symbol. [online] YouTube. Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6jQ7y_qQYUA [Accessed 29 Mar. 2019].
NowThis (2019). Zero Waste Daniel Turns Clothing Scraps Into Fashion | NowThis. [online] YouTube. Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2qqiKNzwHMg [Accessed 29 Mar. 2019].
VICE News (2019). Fashion’s Crippling Impact On The Environment Is Only Getting Worse (HBO). [online] YouTube. Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ECkLgq2W9RU [Accessed 29 Mar. 2019].